Mato Grosso has an area of 903,000 km² and its territory includes 3 biomes: Amazonia, Cerrado and Pantanal.
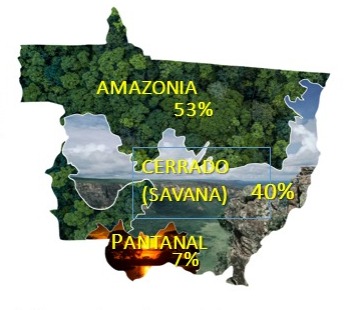
The state still has 62% of its native vegetation cover, which is equivalent to the sum of the area of New Zealand, Denmark and the United Kingdom.
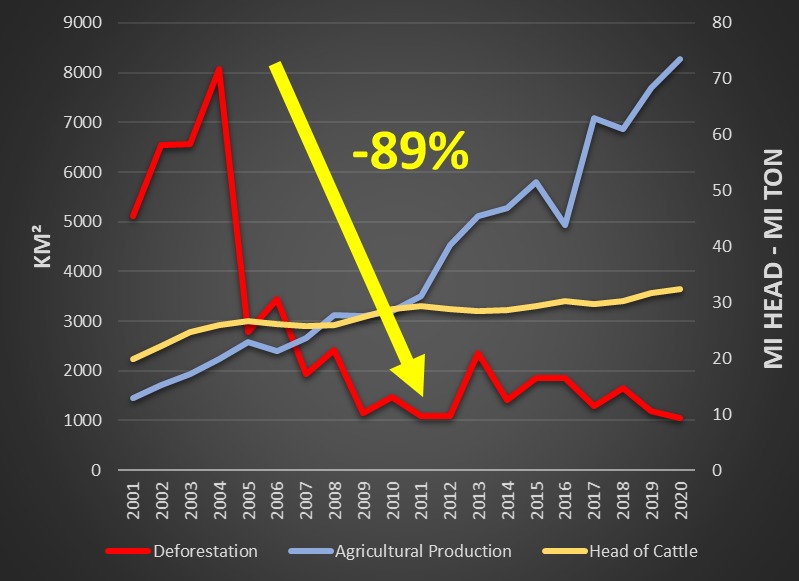
The state reduced deforestation by 89% between 2004 and 2011 and agricultural production had a significant increase, proving that it is possible to produce sustainably.
THE RURAL ENVIRONMENTAL REGISTRY - CAR
The Rural Environmental Registry - CAR is a nationwide electronic public record, which is mandatory for all rural properties. Its purpose is to integrate environmental information from rural properties and possessions related to Permanent Preservation Areas - APP, of restricted use, of Legal Reserve, remnants of forests and other forms of native vegetation, and of areas with agricultural use, composing a database for control, monitoring, environmental and economic planning and combating deforestation.
Each registration undergoes technical analysis to validate whether the data provided and the area without native vegetation are in accordance with the percentages and rules described in the Brazilian Forestry Code.
GOALS
1- To receive, manage and integrate data from all Rural Environmental Registers (CAR) in Mato Grosso;
2- To register and control information on rural properties, referring to their perimeter and location, remnants of native vegetation, Areas of Social Interest, Areas of Public Use, Areas of Permanent Preservation, Areas of Restricted Use, Areas Consolidated and Legal Reserves;
3- To monitor the maintenance, restoration, regeneration, compensation and suppression of native vegetation and vegetation cover in the Permanent Preservation, Restricted Use and Legal Reserve Areas, within rural properties;
4- To promote environmental and economic planning for land use and environmental conservation in Mato Grosso;
5- To make public information available on the environmental regularization of rural properties in Mato Grosso on the world wide web.
Mato Grosso is the state with the largest number of validated Rural Environmental Registers in the country. Of the approximately 137,000 registrations in the Mato Grosso System of Rural Environmental Registration (Simcar), 70% of the area they represent has already been analyzed by the Sema-MT team, while 10% is validated and regular.
ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING
The Coordination of Geoprocessing and Environmental Monitoring (CGMA) of the Secretary of State for the Environment provides a Geo Reference Base.
The cartographic set feeds all the systems used by the secretariat for environmental regularization, licensing, forest management, water resources management and inspection activities.
There are currently 63 reference bases, which are updated with information such as who created the thematic base, data origin, scales, methodology and update date, ensuring the compatibility of the information received and full transparency of SEMA-MT geographic data.
In addition to the vector bases, SEMA-MT provides the image bank of the entire State in a historical series of almost 40 years of mosaics created from images of sensors such as Landsat, Sentinel, RapidEye, CBERS and Planet, in addition to a digital Terrain model ALOS and SRTM.
All data is already georeferenced, allowing the performance of deforestation dynamics and other actions relevant to licensing projects and environmental monitoring.
SEMA-MT, striving for transparency, makes several thematic bases and all titles issued by the agency available to the external public. The information is available on Sema's Geoportal and can be downloaded in different formats, such as .csv, .kml, .shp, among others.
The Geoportal can be accessed here: https://geoportal.sema.mt.gov.br/
Metadata can be obtained here:
http://www.sema.mt.gov.br/transparencia/index.php/sistemas/item/58-portal-de-metadados-geograficos
CHANGE ALERTS FOR VEGETATION COVERAGE
SEMA-MT uses the Plant Coverage Monitoring Platform, which makes it possible to analyze maps, quantitative data and graphics on the situation and dynamics detected in the native vegetation cover.
The tool is available here: https://alertas.sccon.com.br/matogrosso/#/dashboard.
Using the filters available on the Dashboard, users can check changes in vegetation by consulting alerts in different areas, such as: Conservation Units, municipalities, Biomes, Indigenous Lands and Settlement Projects located in Mato Grosso territory.
The alerts are obtained through daily images of the PLANET satellites constellation with 3 meters of spatial resolution.
Based on automatic processes, the algorithms select the best images to generate high-resolution, homogeneous information, covering the entire territory, with the least possible presence of clouds.
In addition to the areas of interest, the citizen can carry out consultations according to the type of vegetation removal, with alerts of the types being made available: clear cut, degradation or burn scar, as well as defining specific periods of time for consultations.
Consulting the alerts on the dashboard can also be combined with data from the reference bases and SEMA systems, such as the Mato Grosso Rural Environmental Registry System (Simcar-MT), allowing you to identify the rural properties where the alerts are located, as well as analyzing the dynamics of the rural property with the Planet images available from July 2019 and throughout the project period.
Users can view the identified satellite images immediately before and after the occurrence of the removal of native vegetation, allowing the visualization and confirmation of the removal of native vegetation.
SIGALERTA
SEMA-MT is in the process of finalizing the SIG Alerta platform, which is its own platform, which will subsidize prevention, planning, management and compliance with inspection demands, resulting from the processing of data that will indicate the location, period of occurrence, the type and dimension of alterations in the cover of native vegetation found in the territory of Mato Grosso.
Thus, SigAlerta is a management and refinement system, which operates on optical and radar data, making the combined use of machine learning (via Google Earth Engine) and validation by human interpretation, always in a topologically assisted way (through spatial rules), supported over High-Resolution Planet Data (NICFI).
The entire system runs on images and technology in the public domain, not requiring any type of expense with the acquisition of satellite images or operational software licenses.
System Modules
- Upload/feed module
- Pre-detection Module (refinement/detection)
- Editing/Validation Module
- Visualization/Query Module
- Alert Management Module
- Inspection Module
- Mobile Application (aid for field checks)
- Statistics Module (Dashboard)
- Administration Module (User Management).
Through the compilation of mappings and alerts generated by SEMA/MT and made available by free sources, such as DETER, PRODES, MAPBIOMAS, SAD IMAZON, GLAD and others, the system will consume all reference bases made available by the Coordination of Geoprocessing and Environmental Monitoring – CGMA and the digital processing is carried out automatically through Google Earth Engine. The aggregated alerts are entered into the single base containing all the attribute fields necessary to meet the requirements of the data processing methodology, crossings with the SEMA database and applying the criteria of weights and codes, established in the methodology developed by the SEMA team GPFCD/SEMA-MT.
The system also generates automated reports that speed up the preparation of technical parts and allows classifying inspection demands quickly, allowing preventive action by agents even at the beginning of deforestation.
Figure - Mobile Application
ACTIONS AGAINST DEFORESTATION
Through the application of the methodology developed by the SEMA team, through cross-references with the bases, intelligence was applied to the data and with the use of the platform of high-resolution satellite images and the daily alerts, it was possible to increase the action against deforestation expressively in the last 4 years. Between 2019 and May 2023, it was possible to apply 14,423 notices of infraction using technology as the right arm of the teams. Mato Grosso increased the numbers of fines applied remotely from 1206 in 2018 to more than 5 thousand fines.
Between 2019 and May 2023, 40% of the fines applied in Mato Grosso were done remotely, verifying the precise images of before and after the deforestation carried out, and 60% in person. The fines applied in the period add up to R$ 6.4 billion.
From 2004 to 2022, there was an 83.8% reduction in deforestation, according to Inpe/Prodes data.
The Law Enforcement Dashboard is a MapBiomas initiative that collects and compiles data on deforestation permits, sanctions, and embargoes issued by the Brazilian federal and state governments' environmental agencies. The analyses presented here aim to monitor how much of the deforestation verified and published by Mapbiomas Alerta was authorized or enforced by these state agencies.
The last published report points Mato Grosso as the State that has the highest record of inspection or authorization action on deforestation alerts.

